A filesystem is a method and data structure that an operating system uses to keep track of files on a disk or partition in short, the way the files are organized on the disk. The word is also used to refer to a partition or disk that is used to store the files or the type of the filesystem.
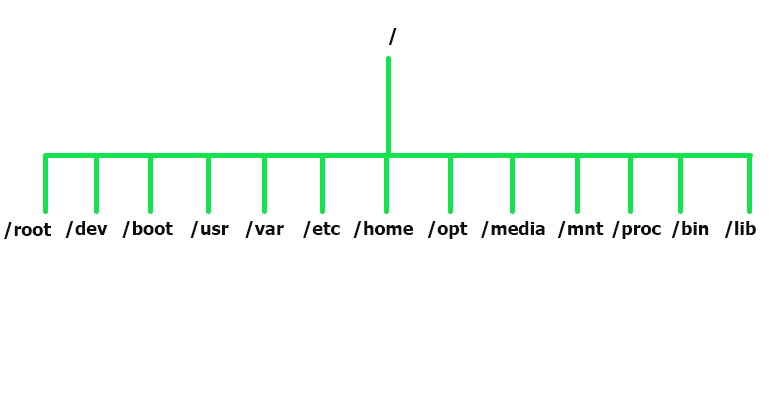
- / :
It is the Top level root directory for all the child directories. Everything starts from the root directory, represented by /, and then expands into sub−directories instead of having so−called ‘drives’. It is represented with forward slash (“/”). - /root:
root users home directory which is not same as ‘ / ‘ only root users has write privilege under this directory. - /dev :
It contains devices files , This includes terminal devices like /dev/sda, usb or any other devices attached to the system. Similar like device manager in windows. - /boot:
It contains system bootable files, kernel related information and bootloader information - /usr:
It contains binaries and loaders, and by default software’s are installed in /usr directory
–> /usr/bin contains binary files for user programs ex. Awk,less,scp
–> /usr/sbin contains binary files of system administrators ex: cron,ssh.useradd
–> /usr/lib contains libraries for /usr/bin and /usr/sbin - /var: It contains variables file information, such as
–> system logs files will be in /var/log
–> databases files in /var/lib/mysql/
–> email s in /var/mail
–> temp files in /var/tmp - /etc:
It contains all system configuration files information like
–> /etc/resolv.conf
–> /etc/logrotate.conf
–> /etc/hosts - /home:
it is home directory for other users except root user , other users to store their personal information and provides working environment for users.
–> /home/Rajkumar
–>/home/ctrls - /opt:
It is optional directory for users, consists of third party software’s. - /media :
It contains all removable media devices like cd-rom, pen drive - /mnt:
It is temporary mount directory where sysadmins can mount file systems ,and it is empty by default. - /proc :
It contains information about system process,this is virtual file system with text information about system resources.
–> Ex: /proc/meminfo, /proc/cpuinfo, /proc/uptime - /bin:
It contains binary executables and contains commands used by all users ex. Ls , ping ,grep cp - /sbin:
It is just like /bin this also contains binary executables but commands under this directoy are used by system administartors for system maintenance purpose.
–> Ex: fdisk, iptables, reboot, ifconfig - /lib:
It contains library files that supports the binaries located under /bin and /sbin
