To log on to a system, a user is required to authenticate himself with a password for the purposes of accounting, security, logging, and resource management.
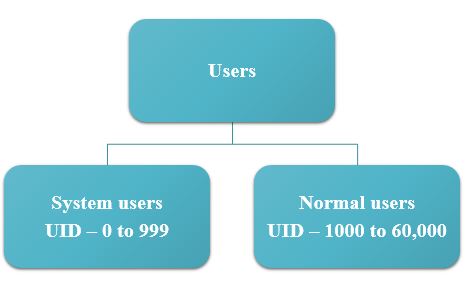
Types of users:
Creating a User:
[root@webnoidschools ~]# useradd <username>
[root@webnoidschools ~]# useradd <options> <arguments> <username>
Options
-u UID
-g Primary group
-o Override
-G Secondary group
-c Comment
-d Home directory
-s Shell
Example:
useradd -g john -c “new user” -d /home/ -s /bin/bash john
User Password
Creating or changing a user’s password
[root@webnoidschools ~]# passwd username
To find a user’s password encryption tool
[root@webnoidschools ~]# passwd -S
User Database Files:
The information regarding the user is stored in the following files:
/etc/passwd
/etc/shadow
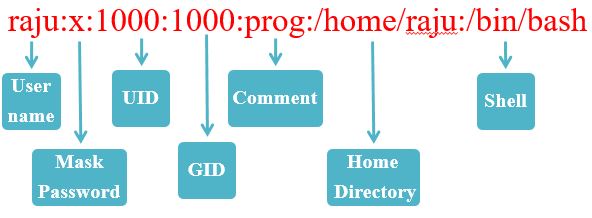
Content of /etc/passwd
- The information of each user created is stored in a separate line in the file /etc/passwd.
- Each record has seven fields separated by a : as given:-
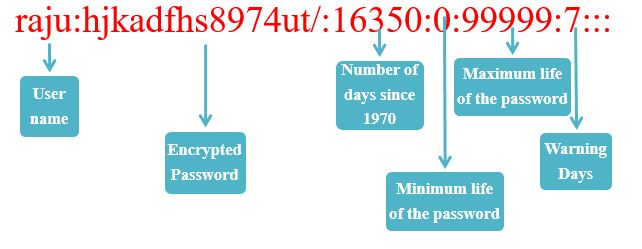
Content of /etc/shadow
- This file contains the encrypted user password.
- Passwords are encrypted using SHA 512 default which can even be change
USERS:
When a user is created in Linux/UNIX, the following are also created by default:
- Home directory /home/[username]
- Mail account /var/spool/mail/[username] (if mail services are running)
- UPG ( User Primary group )
Modifying a User
Modifying user properties
[root@webnoidschools ~]# usermod <options> <arguments> <username>
Options
- -l Change the login name
- -L Lock the account
- -U Unlock the account
Note: All options of ‘useradd’ command can be used with ‘usermod’
To lock the user account:
usermod -L jhon
To unlock the user account:
usermod -U jhon
Deleting a User:
[root@webnoidschools ~]# userdel <options> <arguments> <username>
Options:
-r recursively (deletes the home directory and mailbox also)
Example:
userdel -r jhon
