RAID 1:
RAID is a technology that employs the simultaneous use of two or more partitions on the same or different hard disk drives to achieve greater levels of performance and reliability.
It is a fault tolerance mechanism in which the data is not lost even if one of the disk fails.
Types of RAID
- Hardware RAID
- Software RAID
RAID Levels
- RAID 0 (striping without parity)
- RAID 1 (disk mirroring)
- RAID 5 (striping with parity)
- RAID 10 (mirroring with striping)
RAID 0
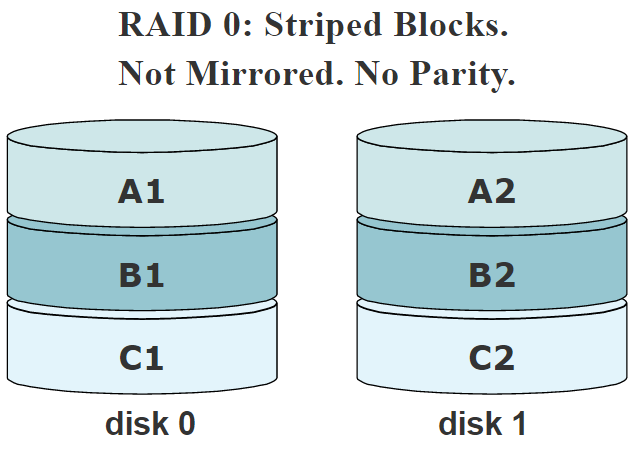
- Minimum 2 hard disks required.
- Can support maximum 32 hard disks.
- Data is written simultaneously and evenly across the multiple hard disks.
- The reading and writing speed is faster.
- Fault tolerance is not available.
RAID 1:
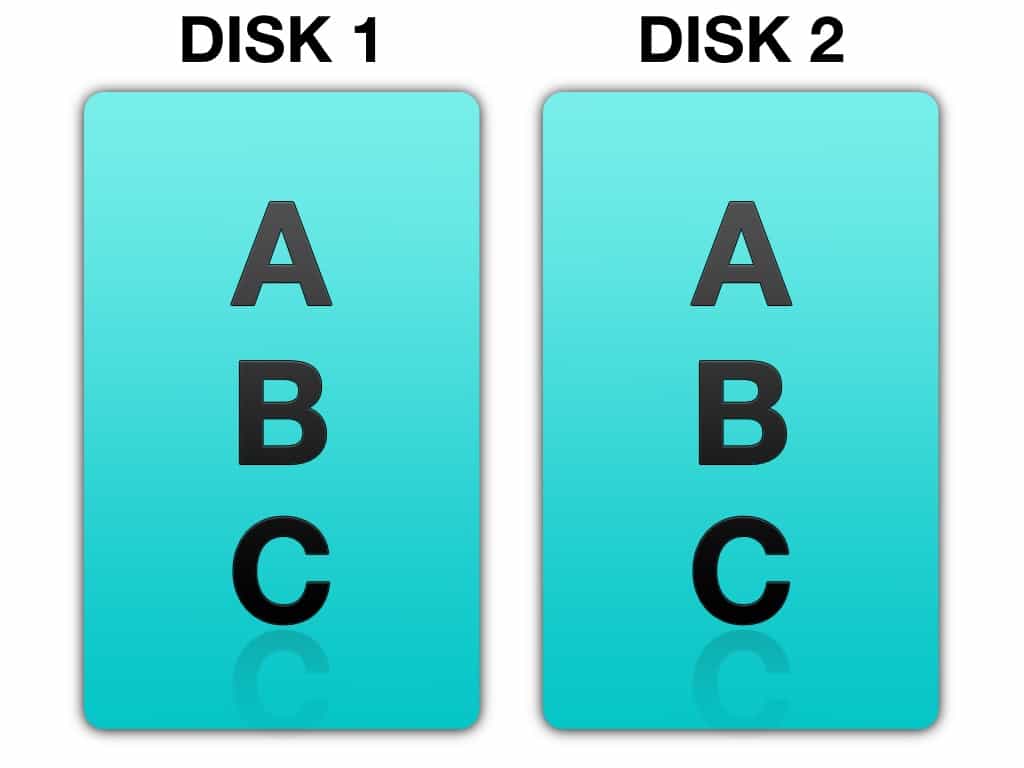
- Works with only 2 hard disks.
- Same data is simultaneous written on both the disk.
- The reading speed is fast and the writing speed is slow.
- Fault tolerance is available.
- Overhead is 50%
RAID 5:
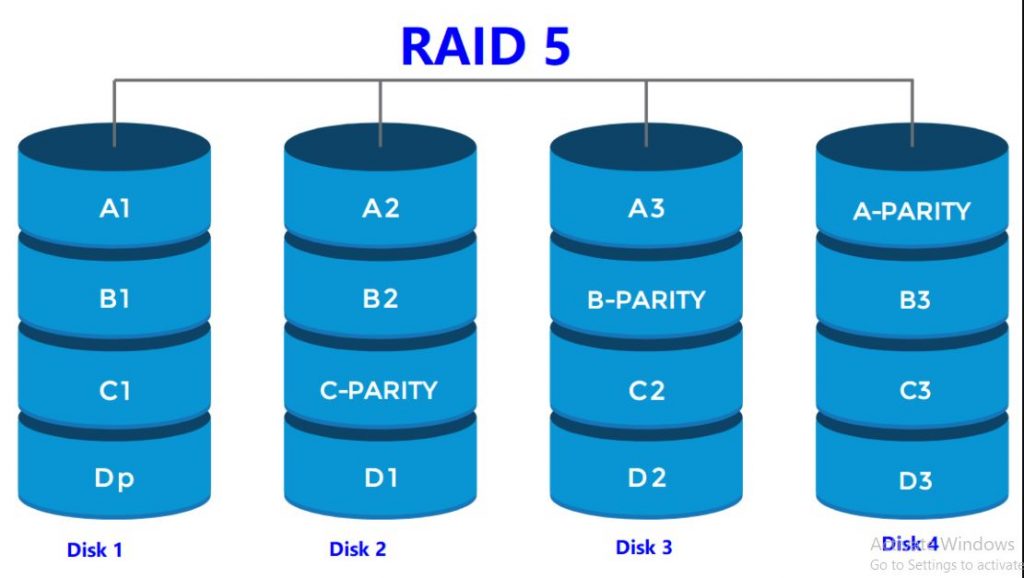
- Minimum 3 hard disks required.
- Can support maximum 32 hard disks.
- Data is written simultaneously and evenly across multiple hard disks.
- The parity is written equally on all disks.
- The reading and writing speed is fast.
- Fault tolerance is available.
RAID 10:
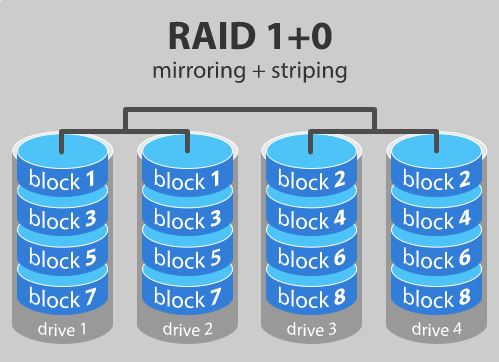
- It requires at least 4 drives
